Dijkstra
최단 거리(shortest path)를 찾는 알고리즘
인접 리스트를 활용해야 시간복잡도, 공간복잡도가 줄어듦
최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
- BFS : 가중치가 없는 그래프에서, 최단 경로를 구할 때
- Dijkstra : 가중치가 있는 그래프에서, 최단 거리를 구할 때
- Floyd-Warshall : 모든 노드 쌍 사이의 최단 거리를 구할 때
- Bellman-Ford : 음수 가중치가 있는 그래프에서 최단 거리를 구할 때
For loop을 이용한 구현 - O(V^2)
과정 설명
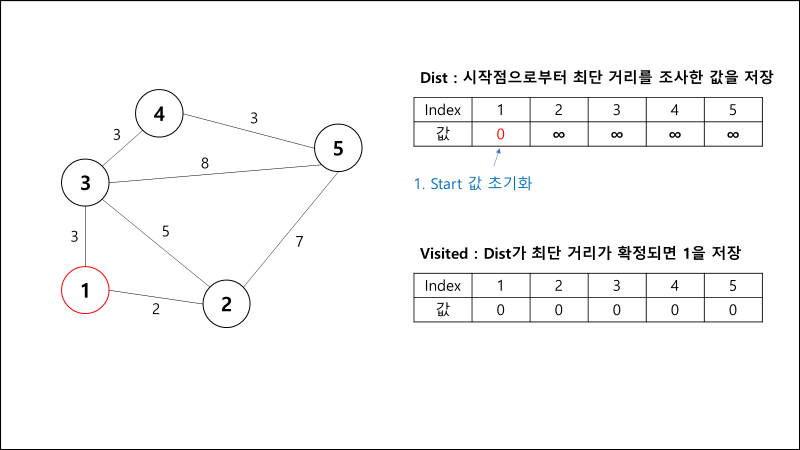
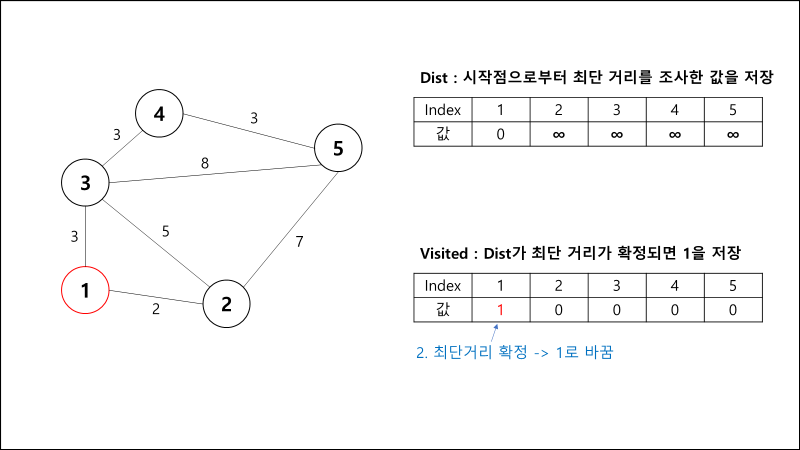
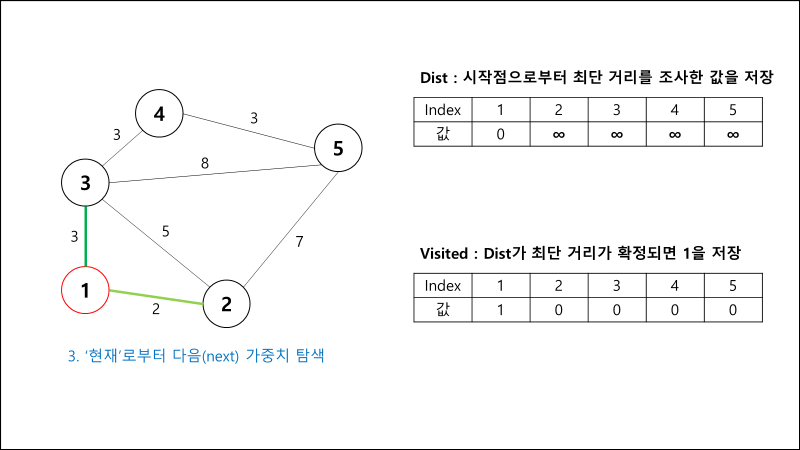
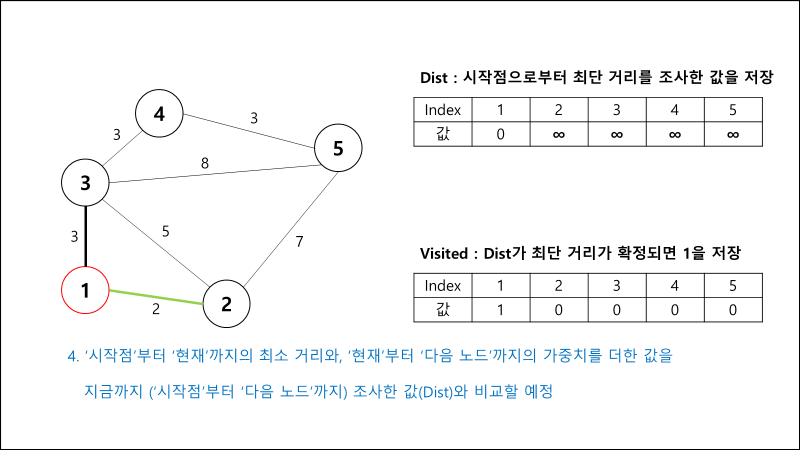
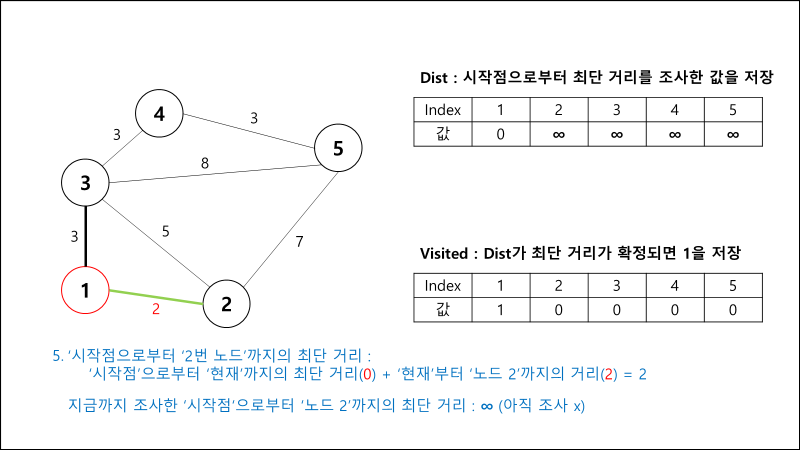
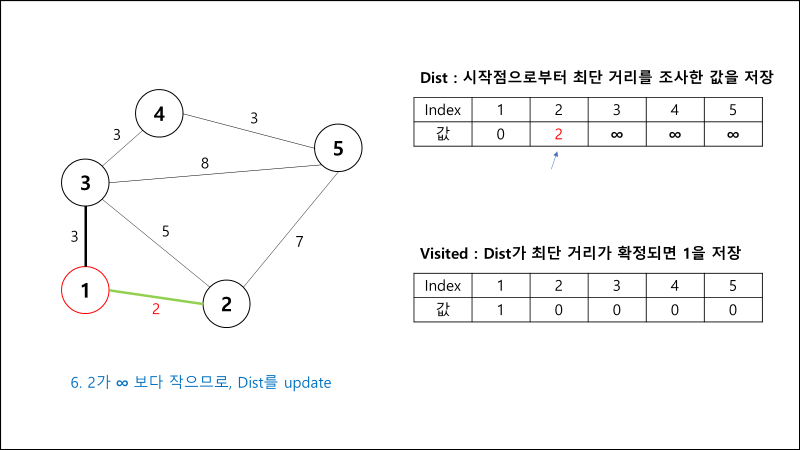
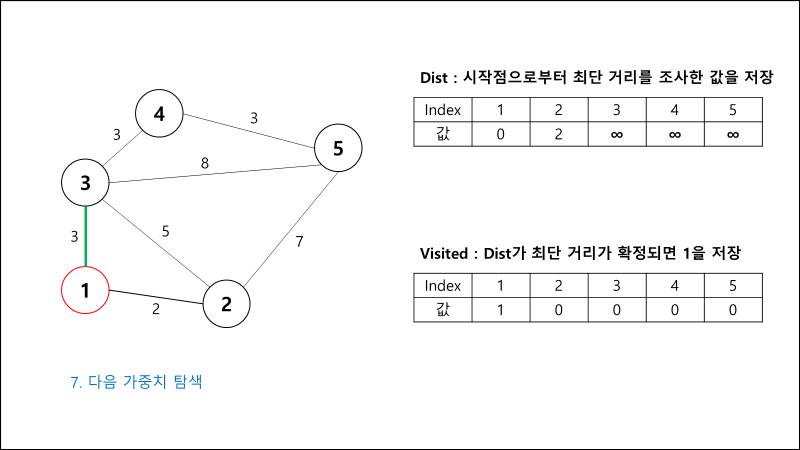
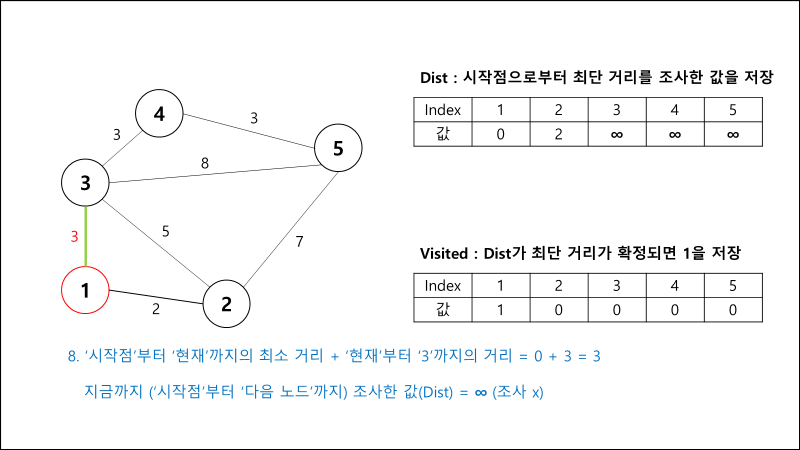
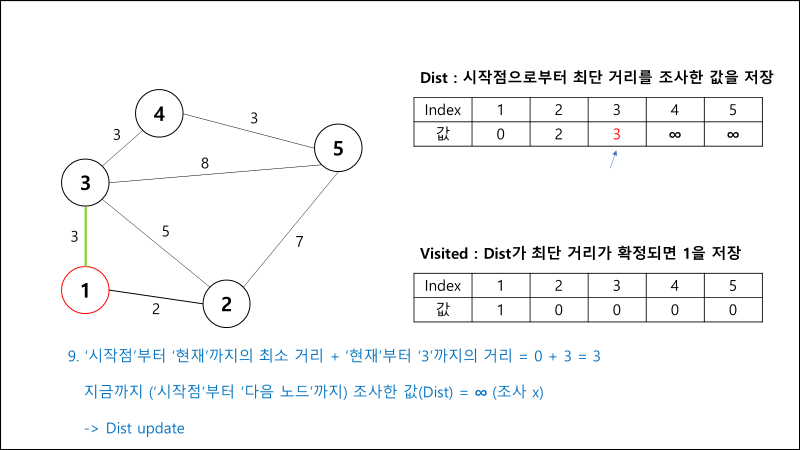
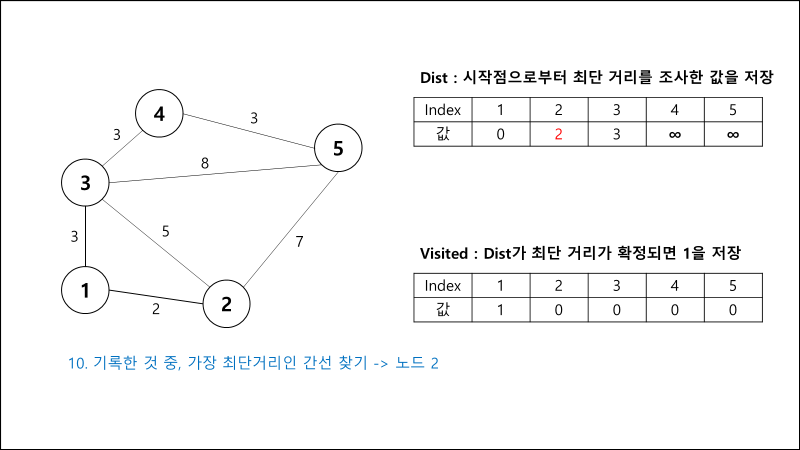
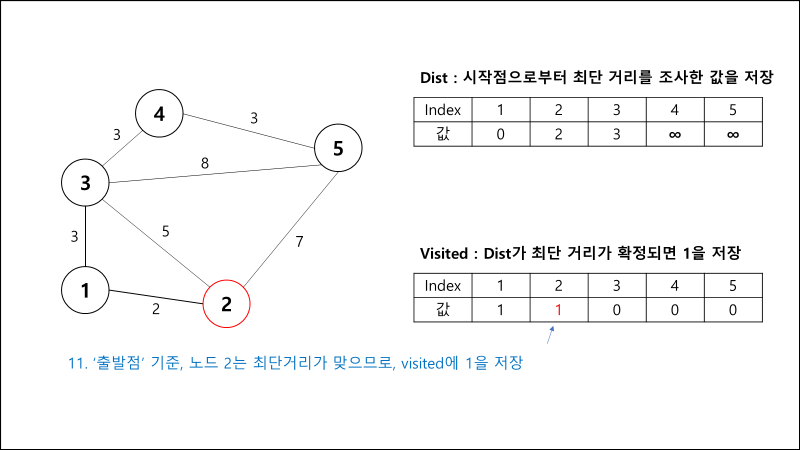
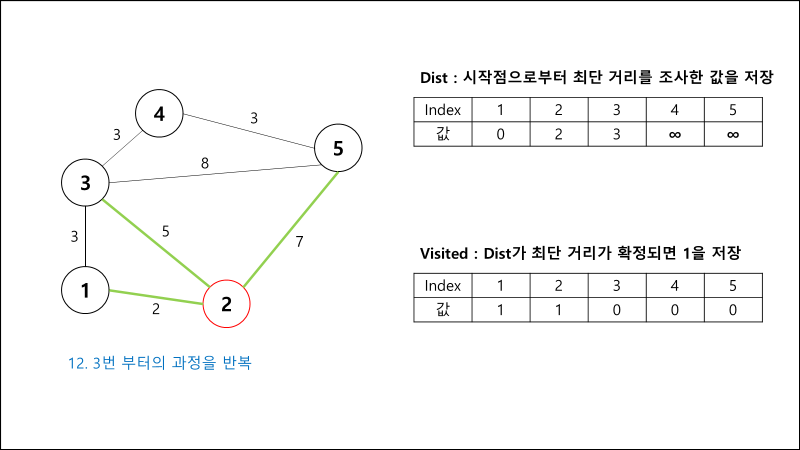
구현 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int to; // 도착 노드
int cost; // 가중치
};
int N, M; // N : 노드의 개수, M : 간선의 개수
vector<Edge>al[100]; // 시작 노드(index), 도착노드(Edge>to), 가중치(Edge>cost) 저장
void dijkstra(int start) {
int dist[100] = { 0, }; // start부터 노드까지의 최단 거리 저장용
int MAX = 21e8; // dist를 MAX로 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
dist[i] = MAX;
}
dist[start] = 0; // 시작 노드부터 시작 노드까지의 가중치(비용)은 0
int visited[100] = { 0, }; // 최단 거리가 확정되었으므로, 방문하지 말라는 표시
// 한 번 돌 때마다, 하나의 노드의 최단 거리가 확정됨
// 왜냐하면, 가장 가중치가 작은 간선부터 처리하기 때문
// -> 모든 노드의 최단 거리가 확정될 때까지 진행
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// 지금부터 가장 가중치가 작은 간선을 찾을 예정
int min_cost = 21e8; // 지금 가장 작은 가중치 찾을 것
int now = -1; // 내가 지금 가려는 노드
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// j번째 노드에 기록된 후보지가 최소값보다 작으면 -> 갱신
if (dist[j] >= min_cost) continue;
// 이미 최단 거리가 확정된 노드라면 -> 다시 갈 필요 없음
if (visited[j] == 1) continue;
// 새로운 최소값을 찾음
min_cost = dist[j];
now = j;
}
// 갱신이 안 되었다 -> 더 이상 바꿀 부분이 없다 -> break
if (now == -1) break;
// now까지의 최단거리 확정
visited[now] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < al[now].size(); j++) {
Edge next = al[now][j];
// 다음 노드까지의 비용 = 지금 확정된 노드까지의 비용(거리) + next까지 가는 비용
int n_cost = dist[now] + next.cost;
// 새로운 경로를 찾았다
// 하지만, 이미 기록된 후보지보다 더 오래걸리는 경로면 쓸모 없다.
if (dist[next.to] <= n_cost) continue;
dist[next.to] = n_cost;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cout << i << "까지의 최단 거리 : " << dist[i] << "\\n";
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int from, to, cost;
cin >> from >> to >> cost;
al[from].push_back({ to, cost });
al[to].push_back({ from, cost });
}
dijkstra(0); // 0번 노드로부터 각 노드까지의 최단 거리
return 0;
}
Priority Queue를 활용한 구현 - O(ElogE)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int to; // 어디 노드로 향하는 지
int cost; // 가중치
bool operator < (Edge next) const {
if (cost < next.cost)
return false;
if (cost > next.cost)
return true;
return false;
}
};
vector<Edge>al[100];
int N, M; // N : 노드의 개수, M : 간선의 개수
void dijkstra(int start) {
// priority queue
priority_queue<Edge>pq;
// 시작 노드를 삽입
pq.push({start, 0});
// dist
int dist[100] = {0, };
int MAX = 21e8;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){
dist[i] = MAX;
}
dist[start] = 0;
// visited
int visited[100] = {0, };
// 구현
// 더이상 갈 후보지가 없을 때까지 반복
while(!pq.empty()){
// 후보지 중 가장 가중치가 낮은 간선을 가져옴
// priority queue => cost를 기준으로 MINHEAP
Edge now = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// 이미 확정된 노드라면, 이 노드에 대해서는 아무것도 안 해도 된다.
if(visited[now.to] == 1) continue;
// now 까지의 최단거리는 확정된다!
visited[now.to] = 1;
// now로부터 갈 수 있는 간선들을 확인
for (int i = 0; i < al[now.to].size(); i++){
Edge next = al[now.to][i];
// n_cost = next까지의 최종 비용
int n_cost = dist[now.to] + next.cost;
// 만약 지금 최종 비용이 이미 기록되어있는 후보 경로의 비용보다 작은 경우만 기록
if (dist[next.to] <= n_cost) continue;
// next까지 가기 위한 새로운 최단 거리를 찾았으니 갱신
dist[next.to] = n_cost;
// 새로운 후보지로 등록
pq.push({next.to, n_cost});
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cout << i << "까지의 최단 거리 : " << dist[i] << "\\n";
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int from, to, cost;
cin >> from >> to >> cost;
al[from].push_back({ to, cost });
al[to].push_back({ from, cost });
}
}
Priority Queue를 활용한 구현 (visited 미활용) - O(ElogE)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int to;
int cost;
bool operator < (Edge next) const {
if (cost < next.cost)
return false;
if (cost > next.cost)
return true;
return false;
}
};
vector<Edge>al[100];
int N, M;
void dijkstra(int start) {
priority_queue<Edge>pq;
pq.push({ start, 0 });
int dist[100] = { 0, };
int MAX = 21e8;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
dist[i] = MAX;
}
dist[start] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
Edge now = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (dist[now.to] < now.cost) continue;
for (int i = 0; i < al[now.to].size(); i++) {
Edge next = al[now.to][i];
int n_cost = dist[now.to] + next.cost;
// 이미 now로 나왔던 노드 -> 첫번쨰 나왔을때 거리가 확정
// 이후에 나온 now와 같은번 노드 = 절대 dist에 기록된 값보다 작을일 없다.
// 만약 now랑 같은 번호가 다시 나왔는데, 이게 dist에 기록된것보다 크면 ->
// 이 전에 이미 확정된 노드이니 -> 여기서부터 더 볼 필요 없다!
if (dist[next.to] <= n_cost) continue;
dist[next.to] = n_cost;
pq.push({ next.to, n_cost });
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int from, to, cost;
cin >> from >> to >> cost;
al[from].push_back({ to, cost });
al[to].push_back({ from, cost });
}
}시간복잡도
최소 모든 간선 한 번씩 : O(E)
모든 간선이 최소 한 번씩은 PQ에 삽입 : O(logE)
E개의 간선이 PQ에서 heapify를 진행 : O(ElogE)
Priority Queue를 활용한 구현(최소 비용 경로 추적)
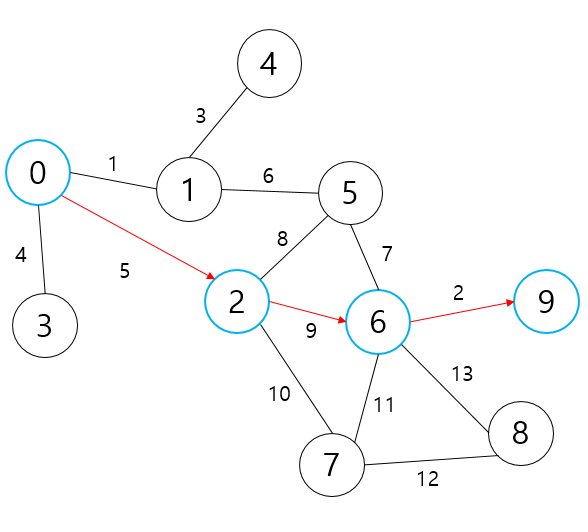
/*
10 13 -> N, M
0 1 1
0 3 4
0 2 5
1 4 3
1 5 6
2 5 8
2 7 10
2 6 9
7 6 11
6 9 2
6 8 13
7 8 12
5 6 7
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int to;
int cost;
bool operator < (Edge next) const {
if (cost < next.cost)
return false;
if (cost > next.cost)
return true;
return false;
}
};
int path[1001];
vector<Edge>al[1001];
int N, M;
void dijkstra(int start) {
priority_queue<Edge>pq;
pq.push({ start, 0 });
int dist[1001] = { 0, };
int MAX = 21e8;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
dist[i] = MAX;
}
dist[start] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
Edge now = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (dist[now.to] < now.cost) continue;
for (int i = 0; i < al[now.to].size(); i++) {
Edge next = al[now.to][i];
int n_cost = dist[now.to] + next.cost;
if (dist[next.to] <= n_cost) continue;
path[next.to] = now.to; // 최적 경로를 역으로 저장해서 업데이트
dist[next.to] = n_cost;
pq.push({ next.to, n_cost });
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int from, to, cost;
cin >> from >> to >> cost;
al[from].push_back({ to, cost });
al[to].push_back({ from, cost });
}
int start = 0;
int end = N-1;
dijkstra(start);
for (int i = end; i != start; i = path[i]) {
cout << i << " "; // 각 노드와 연결된 부분을 출력
}
cout << start;
// End로부터 출력 : 9 6 2 0 //
}만약 최적 경로가 다수일 경우, path를 vector로 정의해서 구현 가능
'IT_Study > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [그래프 #6] MST (Minimum Spanning Tree)를 활용한 문제 풀이 방법 (0) | 2023.02.16 |
|---|---|
| [그래프 #5] 유니온 파인드(Union Find) 알고리즘을 활용한 문제 풀이 방법 (2) | 2023.02.16 |
| [C++] STL : Sorting, Priority Queue 사용법 정리 (0) | 2023.02.13 |
| [C++] 기초 (3) : 문자열(String), 벡터(Vector) (0) | 2023.02.06 |
| [C++] 기초 (2) : 재귀 함수 & 전역변수와 지역변수 & Problem Solving (0) | 2023.01.27 |